The US-China trade war is a complex economic conflict rooted in long-standing issues such as trade imbalances, intellectual property disputes, and geopolitical competition. Originating years ago, tensions escalated sharply in 2025 with steep tariffs imposed by both nations to protect domestic industries and secure strategic technologies.
These tariffs, peaking at an unprecedented 145% on Chinese goods and 125% on US imports, have severely disrupted global supply chains and significantly increased costs worldwide.
For Indian exporters closely tied to this ecosystem, understanding the origins, evolution, and current tariffs is essential to successfully navigate risks and maintain market access.
Read on to explore the timeline, key tariff measures, economic impacts, and implications for Indian exporters.
Key Takeaways:
- Section 232 tariffs were raised to 50% on steel, aluminum, and copper in mid-2025, expanding the scope of US import duties.
- Tariffs of 25% on automobile imports added further pressure on manufacturing and supply chains.
- A 90-day tariff truce capped US tariffs at 30% and Chinese tariffs at 10%, avoiding steep escalation during key trading months.
- The US extended the tariff truce in August 2025 until November 10 to stabilize market conditions through the holiday season.
- China eased some export controls on critical minerals as part of negotiations to de-escalate tensions.
Timeline & Key Events in the 2025 US-China Trade War Tariffs
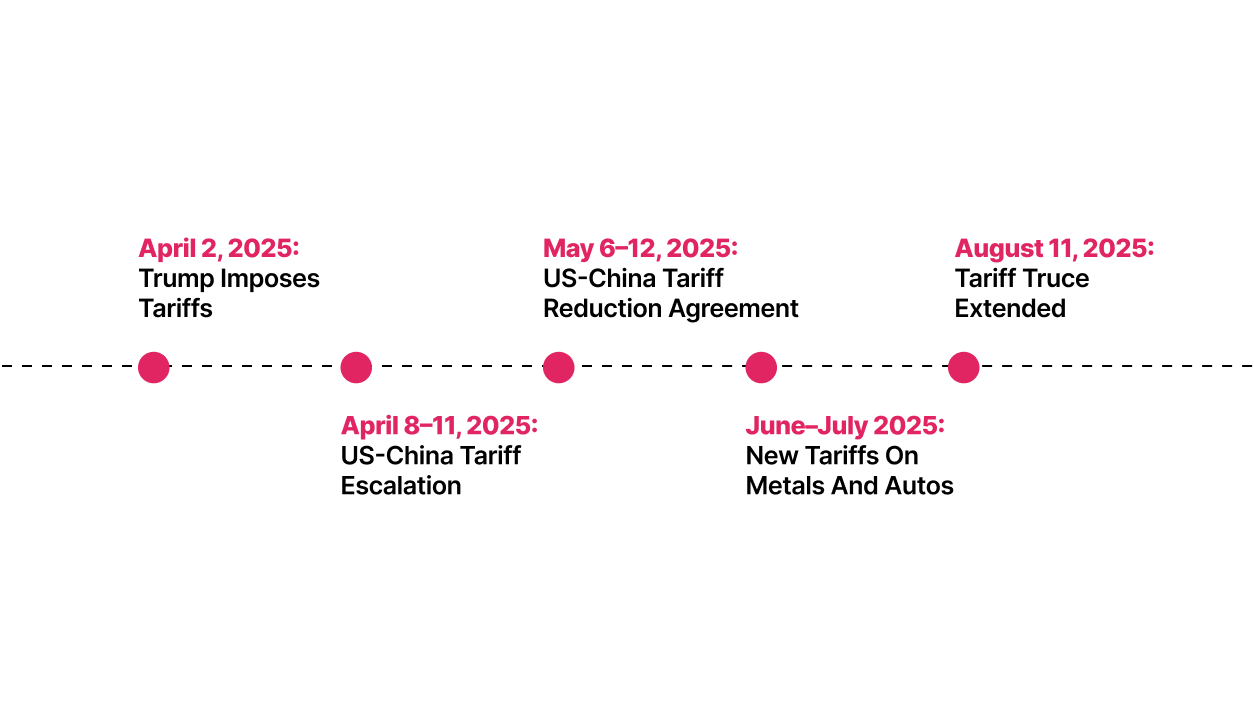
- April 2, 2025: President Trump declares a national emergency on the US trade deficit and imposes sweeping “reciprocal tariffs“ on all major trading partners. Chinese goods face a 34% tariff on top of the existing 20% fentanyl tariffs. A universal 10% baseline tariff is set on nearly all US imports, effective April 5. This announcement triggers market panic and supply chain uncertainty.
- April 8–11, 2025: The US rapidly raised tariffs on Chinese imports from 34% to 84%, then to 125%, ultimately reaching an unprecedented 145%. China retaliates with tariffs up to 125% on US goods, including key sectors like agriculture and technology. Trade tensions and economic disruptions peak during this week.
- May 6–12, 2025: US and Chinese officials meet in Geneva, culminating in an agreement to reduce tariffs for 90 days. US tariffs on Chinese products roll back to 30%, while China cuts theirs to 10%. The fentanyl-related tariffs (20%) remain in place. This pause aims to ease market volatility and enable further trade talks.
- June–July 2025: Additional tariffs are introduced, including 50% duties on steel, aluminum, and copper products under Section 232. The US also enforces a 25% tariff on automobile imports, adding complexity to industrial supply chains.
- August 11, 2025: President Trump signs an executive order extending the tariff truce through November 10, 2025. This move prevents tariffs from surging back to 145%, providing stability during the crucial holiday sales period. Both governments emphasize maintaining economic stability while negotiations continue.
Also Read: Taiwan’s Response to Trump Tariffs and Trade Strategy
Why Did the Trade War Escalate?

The trade war between the United States and China escalated in 2025 due to a convergence of economic, strategic, and political factors.
- Large Trade Deficit and Perceived Unfair Practices: The United States experienced a significant trade deficit with China, estimated at nearly $295 billion in 2024. The US administration viewed this gap as a symptom of unfair trade practices, including forced technology transfers, intellectual property theft, and market access barriers imposed by China.
- Economic Security and National Sovereignty Concerns: Beyond trade figures, the US framed the tariffs as necessary to safeguard national security, emphasizing the protection of critical supply chains and technologies.
- Political and Domestic Messaging: Domestic political considerations also shaped the escalation. The tariffs aligned with President Trump’s “America First” agenda, aiming to appeal to constituencies affected by manufacturing job losses and global competition.
- Geopolitical Rivalry and Technology Competition: The trade war is part of a broader rivalry between the US and China over global influence, technological leadership, and economic dominance.
- China’s Countermeasures: China responded by imposing reciprocal tariffs and non-tariff barriers, including export controls on critical raw materials and actions targeting US firms.
CTA: Worried about tariff shocks and shipment delays?
Request Your Door-to-Door FCL Quote
Impact on Indian Exporters & Global Shifts
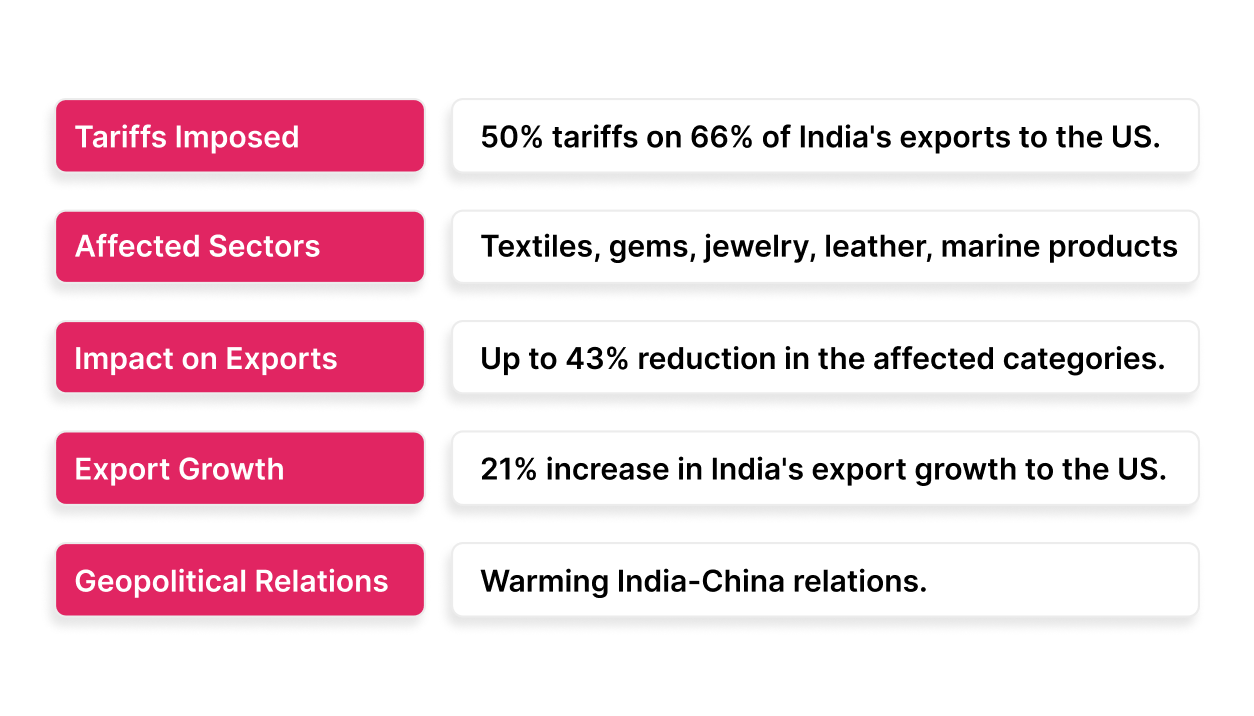
Starting August 27, 2025, the US imposed 50% tariffs on approximately 66% of India’s exports to the US, hitting sectors like textiles, gems, jewelry, leather, marine products, and chemicals hardest. This sudden increase threatens to reduce exports by up to 43% in the affected categories, risking significant revenue losses and job impacts primarily in MSME-driven industries.
India’s export growth to the US had surged 21% earlier in 2025 due to frontloading ahead of tariff deadlines, yet the new tariffs have disrupted this momentum, constraining market competitiveness against rivals such as Vietnam, Bangladesh, and Mexico, who face lower tariff barriers.
While key sectors like pharmaceuticals, electronics, and petroleum products remain largely exempt from tariffs, the broader economic impact is notable. The tariff escalation has introduced uncertainty and operational challenges for exporters and supply chain players, compelling India to fast-track diversification to alternative markets, including the EU and Gulf countries.
Geopolitically, these tariffs coincide with warming India-China relations and signal shifting alliances, further influencing trade routes and diplomatic strategies in the Indo-Pacific region.
CTA: Protect your exports from unpredictable tariffs and delays.
Start Shipping with Intoglo Today
Main Tariff Measures & Products Affected
The 2025 US-China trade war featured sweeping tariffs that targeted a broad range of products across multiple sectors, both in the United States and China.
1. US Tariffs on Chinese Goods
- At their peak, US tariffs on Chinese imports reached up to 145%, impacting diverse product categories including electronics, machinery, solar cells, semiconductors, automotive components, and consumer goods.
- Section 232 tariffs added 50%duties on steel and aluminum products starting June 2025, along with 25% tariffs on automobiles and auto parts, and 50% tariffs on copper and its derivatives, effective from August 2025.
- Some exemptions were granted, notably on semiconductor manufacturing equipment, pharmaceuticals, and electronics, but key industrial and consumer goods remained heavily taxed.
| Product Category | HS Code | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Steel Products | HS Code 7206– HS Code 7216 | 50% tariff (from June 2025) |
| Aluminium Products | HS Code 7601– HS Code 7616 | 50% tariff (from June 2025) |
| Copper & Derivatives | HS Code 7403– HS Code 7404 | 50% tariff (from Aug 2025) |
| Automobiles & Auto Parts | HS Code 8703, HS Code 8708 | 25% tariff (from Aug 2025) |
Also Read: Comprehensive Guide to HS Code 9403: Furniture
2. Chinese Tariffs on US Goods
- China retaliated with tariffs that peaked at approximately 125% in early 2025, though most tariffs were reduced to 10–25% after the May 2025 truce, targeting American agricultural products, energy exports, and manufactured goods.
- Products hit by Chinese tariffs included soybeans, LNG, pork, dairy products, chemical products, and automobiles, typically seeing 10–25% duties under the current policy.
Economic Impact Analysis
The 2025 US-China trade war tariffs have had wide-ranging economic effects across both nations and the global economy.
Trade Flows and Bilateral Trade Value
- US exports to China totaled $143.54 billion in 2024 but declined by 12% between January and April 2025, dropping to $40 billion.
- US imports from China, valued at $462.63 billion in 2024, fell 7% in the first four months of 2025 to $128 billion. This decline marked the first reduction in years, leading to a narrowing of the US trade deficit with China from $95 billion to $88 billion for the same period.
Consumer and Inflation Impact
- Tariffs triggered price increases for American consumers, contributing to a 1.3% rise in the Consumer Price Index (CPI) in April 2025 alone and an estimated total CPI increase of 2.3% for the year.
- The average US household faced an estimated $3,800 reduction in purchasing power due to tariffs, with low-income households disproportionately impacted, losing about $1,700.
GDP and Employment Effects
- The tariffs are estimated to have reduced US GDP growth by 0.5 percentage points starting in April 2025, with a cumulative impact of 0.9 percentage points for the year, equating to a 0.6% smaller economy long term, costing roughly $160 billion annually.
- Regions dependent on manufacturing and agriculture experienced job losses and economic adjustment pains, while some sectors saw temporary employment boosts due to tariff protection.
Chinese Economic Response
- China’s manufacturing sector showed contraction, and exports to the US declined notably. However, monetary easing, fiscal stimulus, and export diversification strategies cushioned the economic blow. China’s GDP growth was projected to slow moderately to 4.8% for 2025, down from 5.4% in Q1.
Also Read:
- Understanding HS Code for Customs Clearance in India
- Understanding Types and Calculation of Shipping Charges
Conclusion
The ongoing US-China trade war and frequent tariff shifts are presenting unprecedented challenges for Indian exporters. Staying proactive is essential for maintaining shipping efficiency and regulatory compliance in a volatile trade environment.
As supply chains adapt, having the right logistics partner is critical for overcoming tariff hurdles, preventing delays, and securing cost control.
If your business needs to move goods from India to the US reliably despite these trade frictions, working with an experienced freight forwarder like Intoglo will make all the difference.
Why Intoglo?
Intoglo is not a marketplace or consultant; it’s your direct logistics partner. With us, you get:
- AI-powered HS code scanning for accurate, compliant documentation
- Clear, no-hidden-cost pricing with up-front, competitive shipping rates
- End-to-end shipment visibility for real-time tracking and control
- Comprehensive support, from customs paperwork to navigating India/USA time zones
- Amazon FBA deliveries and seamless warehousing across the USA
- 24/7 dedicated support across India and the USA time zones
- Door-to-door FCL shipping to simplify operations and avoid complications
With the future of US-China tariffs still unclear, Intoglo’s expertise in cross-border logistics safeguards your exports from regulatory surprises, ensuring reliable and timely deliveries.
Ready to streamline your India-to-USA shipments?
Contact Intoglo’s expert team today for seamless, tailored logistics solutions designed for India’s exporters.
FAQs
Q1. What tariffs has the US imposed on Indian exports in 2025?
The US enforced additional tariffs totaling 50% on approximately 66% of India’s exports to the US—primarily textiles, gems and jewelry, leather, marine products, and chemicals—with some sectors like pharmaceuticals exempted.
Q2. How will these US tariffs impact India’s export volumes?
Indian exports to the US are predicted to decline by up to 43% in affected sectors, causing revenue losses and threatening jobs, especially in MSME-dominated industries.
Q3. Are there any exemptions or products not impacted by these tariffs?
Yes, sectors such as pharmaceuticals, electronics (including iPhones assembled in India), and energy products largely remain exempt from the 50% tariffs.
Q4. How is India responding to these tariff challenges?
The Indian government supports exporters through financial aid, market diversification efforts, enhanced export credit subsidies, and diplomatic negotiations to ease tensions.
Q5. What can Indian exporters do to mitigate the impact of US tariffs?
Exporters should explore alternative markets beyond the US, optimize supply chain operations, leverage expert freight forwarders for compliance and cost management, and stay informed about evolving trade policies.









Leave a comment