The financial hit is clear. Net farm income continues to lag behind recent peaks. At the same time, production costs are rising, and demand in key markets is shrinking. To cushion the blow, the USDA has allocated $10 billion under the Emergency Commodity Assistance Program. But even government support can’t offset the uncertainty weighing down long-term planning and profitability.
Tariff decisions directly change what crops are grown, where they are sold, and how much producers earn. In this blog, we break down how tariffs are affecting US farmers, what it means for agricultural trade, and how exporters can position themselves amid the disruption.
Key Takeaways
- US farmers are facing major losses as tariff tensions limit exports and shift global demand.
- China, which bought US soybean exports in 2024, is now sourcing more from countries like Brazil and India.
- Retaliatory tariffs are forcing US producers to cut output or switch crops, weakening long-term competitiveness.
- Emergency aid programs cover short-term losses but fail to restore lost international market share.
- These shifts in trade flows are opening new opportunities for agricultural exporters in Asia, especially India.
What Are Tariffs and Why Do They Matter in Agriculture?
Tariffs function as taxes on imported goods, designed to protect domestic industries by making foreign products more expensive. In agriculture, these trade barriers create complex webs of economic consequences that extend far beyond their intended purpose.
With food inflation hitting 3.0% in June 2025, tariff policies directly impact what consumers pay at grocery stores. Behind this surge are strained global food supply chains, heavily influenced by the ongoing US–China trade conflict and shifting US tariff strategies.
When one country imposes tariffs, trading partners typically respond with their own retaliatory measures. This tit-for-tat approach creates what economists call a trade war, where escalating tariffs harm both economies. Agricultural products often become prime targets in these disputes because they represent significant export value and can pressure rural voting constituencies.
The agricultural sector faces unique vulnerability to tariff disputes. Unlike manufactured goods, farm products are perishable and seasonal. You can’t simply store millions of tons of soybeans indefinitely while waiting for trade disputes to resolve. This time sensitivity gives trading partners powerful leverage when they target agricultural exports with retaliatory tariffs.
Key Agricultural Trade Mechanics
Agricultural tariffs typically work through several mechanisms:
- Import duties make foreign agricultural products more expensive for domestic consumers.
- Export restrictions limit how much domestic producers can sell internationally.
- Retaliatory tariffs target specific crops to maximize political and economic pressure.
- Quota systems restrict the volume of agricultural products that can be traded.
These mechanisms create immediate impacts on farmers’ bottom lines. When export markets shrink due to tariffs, domestic supply increases, driving down prices. Simultaneously, input costs for fertilizers, equipment, and other farming necessities may rise if they are subject to import tariffs.
What Tariffs Have Hit US Agriculture Recently?
Since early 2025, a wave of new tariffs has disrupted US agricultural exports on a scale not seen in decades. These actions, led by both the US and its trading partners, have triggered immediate fallout for American farmers.
Recent Tariff Timeline
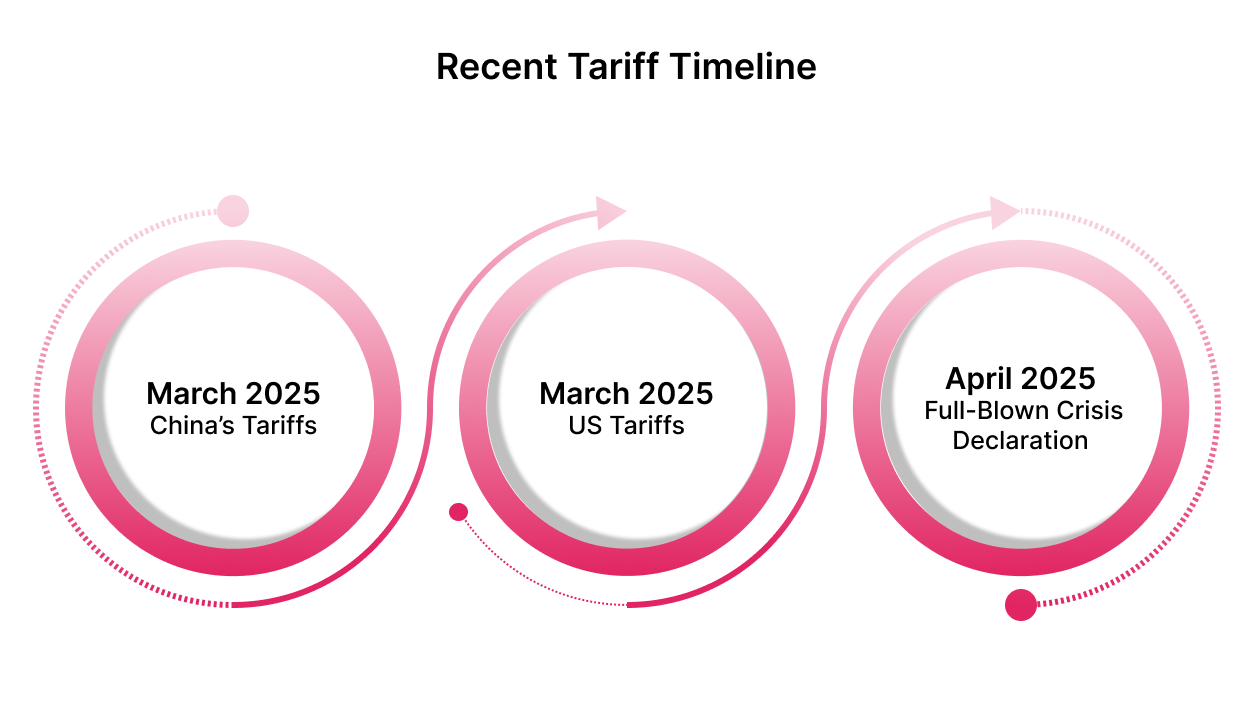
A series of escalations between the US and China has led to a volatile trade environment, with immediate consequences for American farmers.
- March 2025: China implemented 10–15% tariffs on soybeans, corn, and beef.
- March 2025: The US applied 20% additional tariffs on most of the Chinese imports.
- April 2025: US agricultural groups declared a “full-blown crisis” as export orders collapsed.
Specific Commodity Impacts
Major export crops and livestock categories have taken a direct hit, with projected losses threatening long-term competitiveness.
- Soybeans: Potential export losses of over 25 million metric tons.
- Corn: Up to 90% of exports to China could be lost.
- Beef & Pork: Immediate pricing pressure due to reduced Asian demand.
- Wheat: Facing increased global competition as US access shrinks.
Research shows that if China maintains a retaliatory tariff level, the cumulative shock could cripple US agricultural exports to Asia. These numbers represent not just temporary disruptions but long-term structural damage to American farming supply chains.
Want to stay ahead of tariff shifts in your export planning?
Talk to Intoglo’s export specialists nowHow Are Tariffs Affecting US Farmers?
American farmers are experiencing the tariff impact across multiple dimensions of their operations. The financial pressure extends beyond lost export sales to fundamental changes in how farms operate and plan for the future.
US agriculture exporters say the global backlash to Trump’s tariffs is punishing them, primarily through a decline in Chinese buying of US farm products, leading to canceled export orders and layoffs. This represents not just statistical impact but real human consequences in rural communities.
Financial Strain on Farm Operations
Farmers are facing direct cost increases and financial instability. Export cancellations, delayed payments, and commodity price volatility are straining operating capital.
- Input Cost Increases: Fertilizers, machinery, and chemicals now face higher import tariffs, raising production costs.
- Market Price Volatility: Tariff threats create uncertainty in export demand, leading to wide commodity price swings.
- Credit Access: Banks are tightening lending to farms due to higher risk, making capital harder to secure.
- Cash Flow Issues: With fewer export buyers and more delayed contracts, farms struggle to maintain liquidity.
Small and medium-sized farms are especially vulnerable, with many now relying on off-farm income or subsidy programs to stay afloat.
Changes in Planting Decisions
Many farmers are moving away from export-oriented crops as international demand shifts and margins shrink.
- Crop Switching Costs: Moving away from soybeans and cotton toward domestic crops like corn requires retooling equipment, retraining labor, and revising distribution plans.
- Infrastructure Mismatch: Existing storage, transport, and processing systems built for export-heavy crops are now underutilized or inefficient.
Dependency on Government Support
The industry’s dependence on federal aid has surged. In 2024, the American Relief Act allocated $10 billion to stabilize farm incomes.
The situation echoes earlier trade disruptions. During the 2018–2020 trade war, the US government issued billions of dollars in bailouts to keep farms afloat. Today, similar conditions are building, rising costs, disrupted exports, and price volatility are again pushing many farmers below break-even levels.
- These subsidies help farmers manage losses but don’t fix the structural problems behind those losses.
- Industry experts agree that relying on annual bailout programs is unsustainable in the long term.
How Do These Tariffs Affect Global Agricultural Trade?
The ripple effects of US-China tariff disputes extend far beyond these two economies. Global agricultural markets are interconnected, and disruptions in one major trade relationship reshape patterns worldwide.
When Chinese buyers reduce purchases of US agricultural products, they must source these commodities elsewhere. This demand shift benefits producers in Brazil, Argentina, India, and other agricultural exporters while creating oversupply in US markets.
Global Market Disruption Patterns
Global trade patterns are reorganizing fast, with measurable shifts across logistics, pricing, and currency dynamics:
- Supply Chain Rewrites: Decades-old trading relationships are restructured within months.
- Price Movements: Commodity prices adjust quickly to reflect emerging supply-demand realities.
- Route Realignment: Shipping lanes and freight routes adapt to new export-import flows.
- Currency Pressure: Exchange rate volatility further amplifies tariff-driven price impacts.
Brazilian soybeans, for instance, have replaced the US supply in China on a large scale. These new links are sticky; once importers establish a relationship with alternate suppliers, they rarely revert quickly, even if tariffs ease.
Regional Competition Intensification
India is well-positioned to gain from the US-China trade war. Its exporters in rice, pulses, spices, and processed agricultural goods are securing more orders as buyers diversify sourcing.
- Processing Edge: India’s value-added agricultural products are gaining traction in key markets.
- Faster Logistics: Shorter routes to Asia give Indian exporters a cost advantage.
- Favorable FX: The rupee’s position against the dollar and yuan enhances price competitiveness.
- Consistency Focus: Exporters are emphasizing quality control to build longer-term buyer confidence.
Global agricultural trade is entering a more competitive era. Even if tariffs soften, US producers now face stronger contenders across every category, from staples to processed goods.
Indian exporters looking to convert these shifting demand patterns into long-term contracts can use platforms like Intoglo to improve cost-efficiency and shipping reliability.
How Indian Exporters Can Fill the Gap in Global Agricultural Trade?
The disruption in US-China agricultural trade creates substantial opportunities for India across multiple commodity categories. As traditional trade relationships face tariff barriers, importers actively seek reliable alternative suppliers.
Indian agriculture offers several competitive advantages in this new environment. Geographic proximity to major Asian markets provides cost advantages in shipping. Currency exchange rates often favor Indian goods compared to US products. Most importantly, India produces many commodities that directly substitute for US exports.
Specific Commodity Opportunities

- Rice: India’s position as the world’s largest rice exporter becomes more valuable as trade patterns shift.
- Pulses and Legumes: Growing global demand for plant-based proteins benefits pulse shipments.
- Spices and Seasonings: Premium positioning in international markets creates pricing advantages.
- Organic Products: Increasing consumer demand for organic certification benefits Indian producers.
- Processed Foods: Value-added agricultural products command higher margins than raw commodities.
The key lies in building reliable, long-term trading relationships rather than simply filling temporary gaps. Chinese importers and other buyers want suppliers who can provide consistent quality, reliable delivery schedules, and competitive pricing over multiple seasons.
Building Export Market Share
Leading agri-businesses focus on several strategies to capitalize on these opportunities:
- Quality Certification: International standards and certifications build buyer confidence.
- Supply Chain Reliability: Consistent delivery schedules and quality control systems.
- Financial Stability: Ability to handle large orders and provide trade financing.
- Market Intelligence: Understanding buyer preferences and regulatory requirements.
The timing advantage is significant. While US producers deal with tariff uncertainty, Indian suppliers can offer long-term contracts with predictable pricing. This stability appeals to importers looking to minimize supply chain risk.
Platforms like Intoglo help Indian exporters back these commitments with dependable freight timelines, regulatory clarity, and direct shipping lines with no intermediaries, real-time visibility, making them far more attractive to global buyers seeking consistency.
Want to build stronger US partnerships with reliable delivery?
Contact Intoglo today!How Can Exporters Stay Ahead of Tariff Trends?
Managing tariff exposure today requires more than reactive planning; it demands technology-driven visibility, operational agility, and partnerships with logistics providers who understand complex global trade dynamics.
Traditional quarterly reviews and manual updates are no match for the speed and volatility of international tariff shifts. Exporters need systems that capture real-time policy developments, assess downstream impacts instantly, and translate data into action across every shipment.
Digital Tools Are Now Essential for Trade Execution
To respond effectively to policy shifts, exporters are turning to integrated platforms that monitor trade regulations, forecast demand shifts, and streamline documentation. These tools form the backbone of scalable, compliant, and cost-effective cross-border operations.
- Tariff and Policy Tracking: Automated updates on regulatory changes, tariff revisions, and bilateral agreement developments.
- Dynamic Market Intelligence: Live pricing data, volume forecasting, and demand pattern analytics.
- Compliance Management: Country-specific documentation workflows to meet evolving customs and trade requirements
- Route Optimization: AI-based cost modeling to adjust shipping paths as global conditions change.
Strategic Flexibility Makes Exporters More Resilient
Exporters who succeed in volatile tariff environments build flexible strategies that minimize exposure and create new growth levers.
- Multi-Market Focus: Reducing over-reliance on a single destination by expanding across geographies.
- Product Mix Diversification: Building a broader portfolio across raw, semi-processed, and finished goods.
- Currency and Input Hedging: Limiting financial volatility through smart financial instruments.
- Adaptive Supply Chains: Fast relocation of sourcing and production based on emerging trade advantages.
Looking for an AI-powered HS code scanner and smarter freight routes?
Get in touch with Intoglo!How Intoglo Helps Exporters Respond to Tariff Volatility?
Even the best strategy can falter if execution lacks speed and precision. Exporters need logistics providers who don’t just move goods, but also understand market dynamics, compliance pitfalls, and the technology required to stay competitive.
Intoglosupports exporters with end-to-end, tech-powered logistics that adapt to global trade shifts in real time. The platform combines ocean freight execution with integrated tools for compliance, cost control, and visibility across the entire shipment lifecycle.
Here’s what sets Intoglo apart:
- Complete Door-to-Door Shipping: From origin pickup in India to final delivery across 41,000+ US zip codes, consolidation, customs, warehousing, and last-mile included.
- Instant rate quotes: Accurate rate quotes upfront with no hidden fees to support margin planning.
- Strategic US Warehousing: Access to over 50 US locations with fulfillment options for both B2B and D2C distribution.
- Amazon FBA Shipment: Direct delivery to FBA centers, with all prep work handled by teams trained on Amazon’s specific requirements.
- AI-Driven HS Code Scanner: Smart HS Code tool, proactive customs entry handling, and expert clearance to avoid costly delays.
- Real-Time Visibility with Glotrack: Shipment tracking, alerts, and digital document access, all in one platform.
Backed by experienced customs brokers, strong carrier relationships, and 24/7 bilingual support teams, Intoglo helps Indian exporters convert tariff volatility into competitive advantage.
Conclusion
Tariff policies have triggered real disruptions in US agriculture, lower export volumes, rising production costs, and reduced farm income. These changes are forcing a shift in global supply chains.
For Indian agricultural exporters, this creates a clear opportunity to gain ground in the US market. But short-term wins are not enough. Success depends on consistent delivery, regulatory compliance, and strong logistics support.
Intoglo offers end-to-end FCL solutions built for this kind of environment. From instant rate quotes to full shipment tracking, we help Indian exporters manage complexity and grow with confidence.
Want to expand into the US with fewer delays and more control? Contact Intoglo now to streamline your agricultural exports.
FAQ’s
1. Were farmers hurt economically by high tariffs?
Yes, high tariffs led to reduced export demand, lower crop prices, and income losses. US farmers, especially soybean growers, faced major setbacks as trade partners like China imposed retaliatory tariffs on American agricultural products.
2. What did Trump do to farmers?
Trump’s tariff policies triggered retaliatory measures from key trading partners, reducing US agricultural exports. To offset losses, his administration issued billions in aid under programs like the Market Facilitation Program and Emergency Commodity Assistance Program.
3. Is US agriculture in trouble?
Yes. US agriculture faces pressure from shrinking export markets, global competition, and volatile trade policies. Net farm income remains below pre-2022 levels, and long-term international market share continues to erode.
4. Did China stop buying soybeans from the US?
China significantly reduced its soybean imports from the US during peak trade tensions, shifting to Brazil and other suppliers. Although some trade resumed, US exporters have not fully regained their earlier market share.
5. Do farmers benefit from free trade?
Yes. Free trade allows farmers to access global markets, sell at competitive prices, and expand production. Trade restrictions, on the other hand, often limit demand and reduce profitability for export-reliant crops like soybeans, corn, and wheat.









Leave a comment