In 2025, U.S. President Donald Trump announced a plan to match India’s high tariffs, imposing a 50% tariff on a wide range of Indian goods. This decision has sent shockwaves through India’s export sectors, particularly textiles, gems, and auto parts, as businesses face increased costs and reduced competitiveness in the U.S. market.
As the two countries engage in ongoing trade talks, the stakes are high for India’s trade relations with the U.S. and the future of its export industries.
This article explores the impact of Trump’s tariff strategy on Indian exports and what India can do to respond.
Key Takeaways:
- Trump’s proposed 50% tariffs threaten $48B of Indian exports to the U.S.
- India ranks sixth in global textile exports, and higher duties may reduce U.S. orders.
- Gems and jewelry face tariffs up to 50% which could slow India’s highest earning export sector.
- Auto parts shipments to the U.S. make up 27% of the trade and carry higher compliance costs.
- The IMF warns India’s GDP could fall by 0.8% if trade tensions continue.
What Does It Mean That Trump Will Match India’s High Tariffs?
In August 2025, President Donald Trump implemented a 25% reciprocal tariff on Indian imports, effectively matching India’s average tariff rate of 12%. This move was part of his administration’s broader strategy to address trade imbalances and pressure countries into reducing their own tariffs.
The reciprocal tariff policy aims to create a level playing field by imposing tariffs on countries with higher trade barriers against U.S. goods.
Subsequently, an additional 25% tariff was imposed on Indian goods due to India’s continued purchases of Russian oil, bringing the total U.S. tariff on Indian imports to 50%.
This penalty was justified under the International Emergency Economic Powers Act, citing national security concerns related to India’s energy trade with Russia.
The Economic Impact of Trump Matching India’s High Tariffs
President Trump’s decision to impose tariffs on Indian goods has significant economic implications for India. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Immediate Financial Losses for Indian Exports
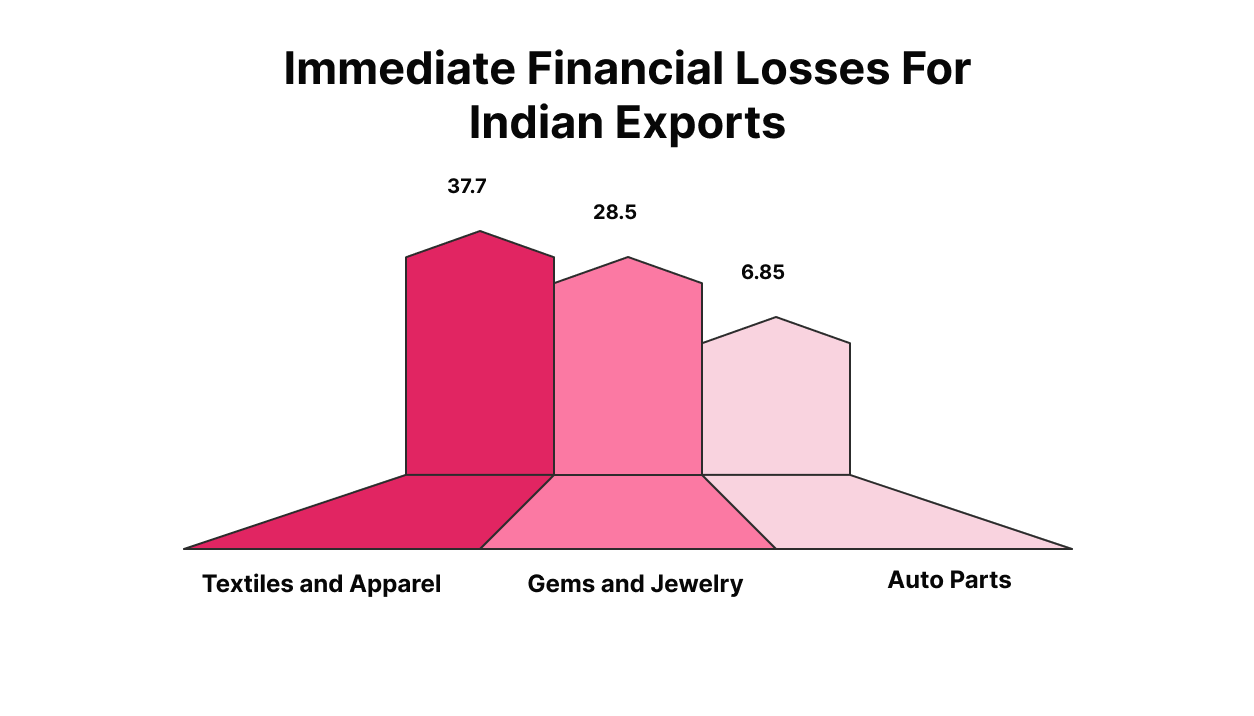
- Value of Affected Exports: Approximately $48.2 billion worth of India’s merchandise exports to the United States are now subject to the 50% tariff. (The Economic Times)
- Key Sectors at Risk:
- Textiles and Apparel (HS Code 6109): India’s textile and apparel sector, including handicrafts, made up 8.63% of total merchandise exports in 2024–25 ($37.7B). As the 6th largest textile exporter globally, India faces heightened risk if US tariffs tighten.
- Gems and Jewelry (HS Code 7102): India’s gem and jewelry exports stood at $28.5 billion in FY25.
- Auto Parts (HS Code 8708): India exported $6.8–6.9 billion in automotive goods to the U.S. in FY2024, representing 27% of India’s total auto exports.
Long-Term Economic Consequences
- Potential GDP Impact: Analysts estimate that if the tariffs remain in place for an extended period, India’s GDP could decline by up to 0.8%.
- Trade Diversification: To mitigate the impact, India is exploring alternative markets and strengthening trade relations with other countries.
Impact on U.S. Companies
- Increased Costs: U.S. companies that rely on Indian imports for raw materials and components may face higher costs, potentially leading to increased prices for consumers.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: The tariffs could disrupt established supply chains, affecting industries such as automotive and electronics that depend on Indian exports.
Secure your supply chain with Intoglo’s door-to-door FCL ocean shipping.
Get a QuotePolitical and Diplomatic Reactions to Trump’s Tariff Strategy
President Trump’s decision to impose a 50% tariff on Indian goods has significantly strained U.S.-India relations. Here’s how both nations are responding:
U.S. Political Objectives Behind the Tariffs
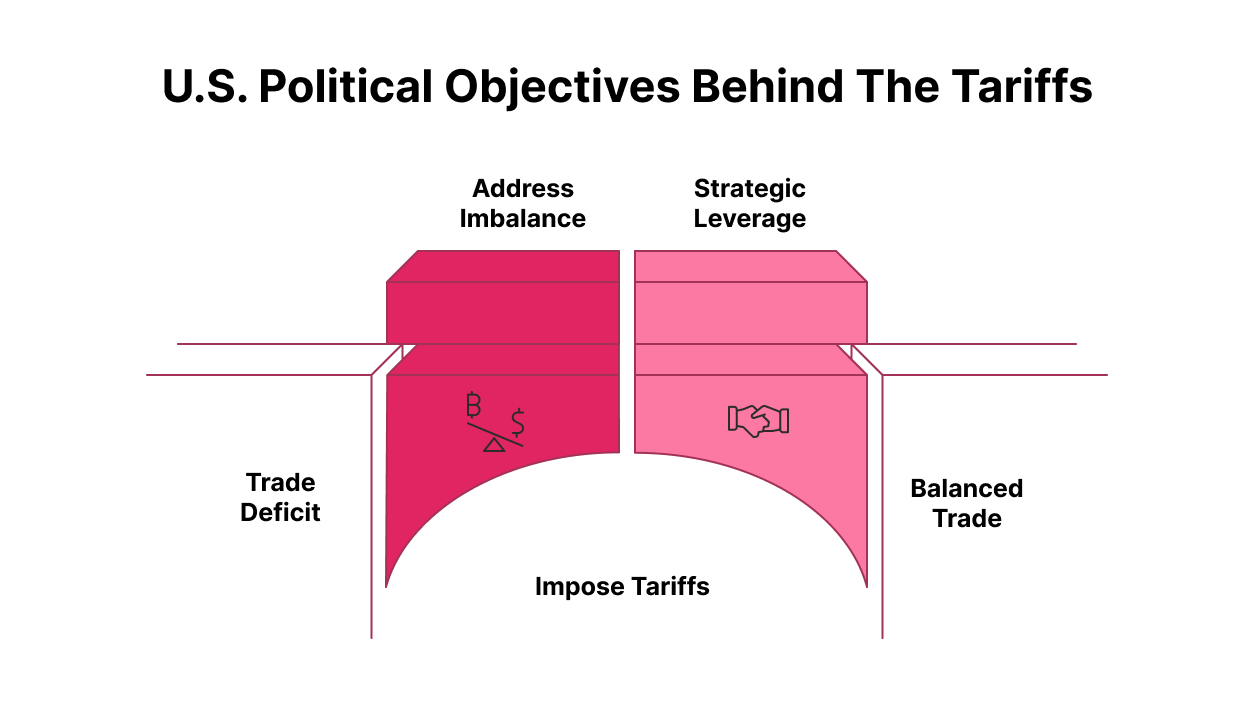
- Trade Deficit Concerns: Trump’s administration has expressed concerns about the U.S. trade deficit with India, which was $45.7 billion in 2024. The tariffs are seen as a measure to address this imbalance.
- Strategic Leverage: The tariffs are also viewed as a tool to press India into aligning more closely with U.S. geopolitical objectives, particularly regarding energy imports from Russia.
India’s Diplomatic Response
- Strong Condemnation: India has labeled the U.S. tariffs as “unfair,” “unjustified,” and “unreasonable,” emphasizing its right to secure energy supplies for its population. The Times of India
- Strategic Autonomy: The Indian Ministry of External Affairs reiterated that its energy policy is driven by national necessity and that the U.S. continues to engage in trade with Russia, highlighting a perceived inconsistency in the application of sanctions.
Impact on U.S.-India Strategic Partnership
- Defense and Security Ties: Reports suggest that India has paused major defense procurements from the U.S., though the Indian Defence Ministry has denied these claims, emphasizing that existing acquisition processes remain on track. Wikipedia
- Regional Cooperation: The tariff dispute has raised concerns about the future of strategic cooperation, including joint regional initiatives like the Quad, with experts warning that the fallout could unsettle mutual trust and complicate defense ties. Wikipedia
Trade Negotiations and Bilateral Trade Agreement (BTA)
- Postponed Talks: The sixth round of BTA talks, scheduled for August 25–29, 2025, has been postponed amid the tariff escalation. India’s refusal to open its agricultural market was a significant sticking point.
- Continued Engagement: Despite the setbacks, both nations have expressed a desire to continue negotiations, with India emphasizing the importance of the strategic partnership beyond trade issues.
Also Read: Why Is Trump Threatening India Over Tariffs? A Strategic Guide for Exporters
India’s Strategic Response to Trump’s Tariffs: Mitigation and Adaptation

In the face of the U.S. tariff on Indian goods, India has initiated a multifaceted strategy to mitigate the impact on its export sectors and adapt to the evolving trade landscape.
1. Strategic Trade Negotiations and Bilateral Engagement
- Pursuit of Free Trade Agreements (FTAs): India is actively pursuing FTAs with key partners to enhance market access and reduce trade barriers. Notably, India signed the Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA) with the United Kingdom on July 24, 2025, marking a significant milestone in bilateral trade relations.
- Engagement with the European Union (EU): India is also in discussions with the EU to finalize a Free Trade Agreement, aiming to bolster trade ties and provide Indian exporters with preferential access to European markets.
2. Targeted Financial Support for Export Sectors
- Sector-Specific Credit Lines: The Indian government is considering the introduction of sector-specific credit lines with relaxed collateral requirements to support industries most affected by the tariffs, such as textiles, gems and jewelry, and auto parts.
- Enhanced Export Promotion Initiatives: Efforts are underway to enhance export promotion through digital platforms, trade events, and export incentives, aiming to streamline processes and expand market reach.
3. Diversification of Export Markets
- Exploring New Markets: India is focusing on diversifying its export destinations to reduce dependence on the U.S. market. Initiatives include promoting exports to regions such as ASEAN, the European Union, and Africa.
- Sectoral Diversification: Specific sectors, like seafood, are being encouraged to expand their market reach to destinations such as the EU, Japan, South Korea, the UK, Russia, Australia, West Asia, and Southeast Asia.
Also Read: Understanding Tariff Authority for Major Ports
4. Strengthening Domestic Capabilities
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Schemes: India is implementing PLI schemes across various sectors, including textiles, electronics, and pharmaceuticals, to boost domestic manufacturing and reduce reliance on imports.
- Infrastructure Development: The government is investing in logistics infrastructure, including the development of district export hubs and e-commerce export hubs, to facilitate smoother export processes and reduce costs.
Cut delays and ship tariff-ready with Intoglo’s India–USA logistics solutions.
Contact UsWhat Does This Mean for Indian Exporters?
1. India’s export strength increases exposure
- Textiles (HS 6109): worth $37.7B in 2024–25, accounting for 8.6% of exports. India ranks 6th globally.
- Gems and jewelry (HS 7102): the world’s top diamond processor, with billions in exports of polished stones and gold jewelry.
- Auto parts (HS 8708): a fast-growing category, with the US as a key buyer.
2. Tariff hikes put margins at risk
- Higher duties on textiles could erode India’s competitive edge in the US.
- Gems face potential tariff hikes of 26–50%, directly hitting India’s top export earner.
- Auto parts exports risk shrinking profitability under new duty structures.
Why it matters for D2C and Amazon sellers?
Rising tariffs don‘t just affect large exporters. Smaller brands and sellers face tighter margins, shipping delays and tougher compliance. The right logistics support becomes critical to stay profitable.
Intoglo helps exporters stay resilient.
- Door-to-door FCL ocean shipping from India to the USA.
- AI-powered HS Code scanner for accurate classification and compliance.
- Warehousing and Amazon FBA integration for seamless delivery.
Conclusion
The ongoing tariff escalation between the U.S. and India represents a significant challenge for Indian exporters. However, strategic responses such as trade negotiations, financial support for vulnerable sectors, and market diversification can help mitigate the impact of these tariffs. By taking proactive steps, Indian exporters can continue to thrive in a changing trade environment.
This is where Intoglo comes in. With transparent pricing, real-time shipment tracking, and AI-powered compliance tools, Intoglo provides exporters with the visibility and support needed to navigate complex tariffs and shipping challenges.
Contact Intoglo’s expert team today to learn how we can simplify your shipping process, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with U.S. import regulations.
FAQs
Q1: How will Trump’s 50% tariffs affect India’s exports?
A1: Trump’s tariffs will significantly increase costs for Indian exporters, especially in sectors like textiles, gems, and auto parts. These higher costs may reduce India’s competitiveness in the U.S. market, leading to potential market share loss to countries with lower tariffs.
Q2: Which Indian industries will be most affected by the tariffs?
A2: Industries such as textiles, gems and jewelry, and auto parts will face the brunt of the tariff hikes. These sectors account for a substantial portion of India’s exports to the U.S., and the tariffs will make their goods more expensive for U.S. consumers.
Q3: Can India negotiate its way out of these tariffs?
A3: Yes, India is actively negotiating with the U.S. to address these tariffs. India is also pursuing Free Trade Agreements and looking to diversify its export markets to reduce dependency on the U.S. market. Diplomatic talks continue to be a crucial aspect of this ongoing trade dispute.
Q4: How can Indian exporters mitigate the impact of these tariffs?
A4: Indian exporters can mitigate the impact by diversifying export markets, seeking financial support from the government, and using tech-driven solutions like Intoglo for better visibility, compliance, and transparent pricing in their shipping processes.
Q5: Will these tariffs have a long-term impact on India’s economy?
A5: The long-term impact could be significant, with some experts predicting a 0.5% decrease in GDP if the tariffs persist. Sectors most affected by the tariffs, like textiles and auto parts, may face slow growth, which could lead to job losses and reduced industry output.









Leave a comment