The US-China trade war, escalating in 2025, has brought unprecedented tariffs on civilian aircraft, a sector that was historically exempt from such duties since a 1980 free trade agreement.
With the US imposing a 145% tariff on Chinese imports and China retaliating with a 125% tariff on US goods, including Boeing jets, this conflict has disrupted global aerospace supply chains and forced Chinese airlines to halt deliveries and return aircraft to the US.
This article delves into the timeline and reasons behind the tariffs, explores the impact on Boeing and international aviation supply chains, examines the responses from both countries, and discusses the broader implications for exporters, manufacturers, and logistics providers worldwide.
Key Takeaways:
- The 2025 US-China tariffs ended four decades of tariff-free civilian aircraft trade.
- Chinese airlines halted Boeing deliveries, causing significant backlog and revenue uncertainty.
- Redirecting jets to new markets involves high customization and contractual challenges.
- Global aerospace supply chains face rising costs and delays due to tariff disruptions.
- Airbus is gaining market share in China amid Boeing’s delivery setbacks.
How US-China Tariffs on Civilian Aircraft Are Reshaping Boeing’s Global Outlook
The imposition of stiff US-China tariffs in 2025 has fundamentally shifted the landscape for civilian aircraft trade. Boeing, historically a major supplier to China, now faces delivery freezes and market uncertainty, with significant ripple effects for exporters, supply chain managers, and logistics providers worldwide.
Halted Deliveries and Returned Aircraft
In 2025, as a direct impact of US-China trade tensions, Chinese airlines were ordered to stop accepting deliveries of new Boeing jets. This unprecedented move resulted in at least two Boeing aircraft being returned to the United States, with more expected to follow.
This halt disrupts a sector that had operated tariff-free for over 40 years, shaking Boeing’s established delivery processes and supply chains.
Impact on Boeing’s Backlog and Revenue
China accounts for roughly 10% of Boeing’s commercial aircraft backlog, representing a significant revenue source now facing sharp uncertainty. Out of Boeing’s global backlog exceeding 6,000 jets, about 50 were scheduled for delivery to Chinese carriers in 2025.
Challenges in Redirecting Jets to New Buyers
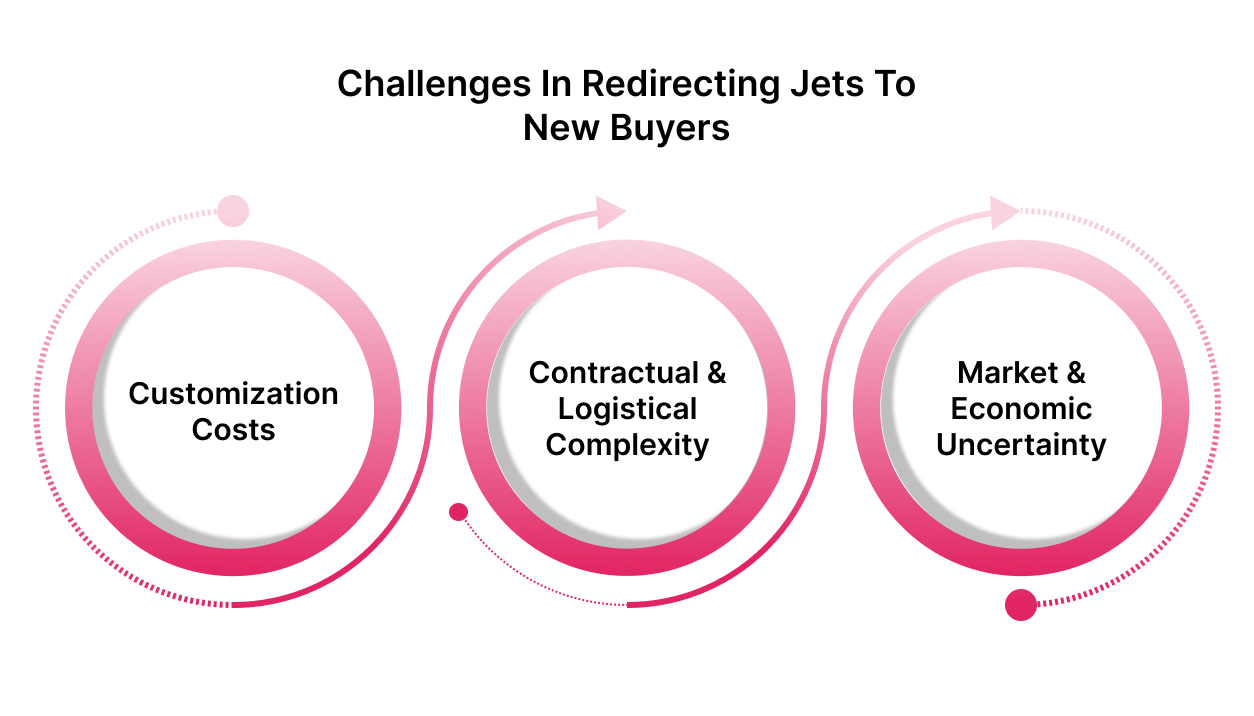
While Boeing aims to place undelivered jets in alternative markets such as India, Latin America, and Southeast Asia, this strategy involves complex hurdles:
- Customization costs: Jets are tailored to each airline’s specific requirements, making quick resale costly and time-consuming.
- Contractual and logistical complexity: Transferring orders involves renegotiations, component adjustments, and buyer approvals, complicating the process.
- Market and economic uncertainty: Demand fluctuations amid the global economic slowdown risk affecting potential new buyers’ commitments.
Boeing Backlog Status Table
| Metric | Quantity | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Total Boeing Backlog | 6,000+ jets | Global pending orders |
| Share for China | ~10% | Significant but reduced share |
| Jets Returned from China | 2+ jets | Delivery freeze initiated |
| Jets Scheduled for 2025 Delivery to China | ~50 jets | Delivery halted |
Also Read: US-China Trade War: A Guide to Understanding Tariff Impacts
Broader Global Supply Chain Impact on Aerospace Manufacturing
The US-China tariff dispute is not only a Boeing story; it reverberates across aerospace manufacturing worldwide.
Complex and Interconnected Supply Chains
The aerospace industry relies on a highly globalized supply chain, with key parts and components sourced from countries including France (engines), Canada, the UK, Japan, and Italy.
The imposition of tariffs on civilian aircraft and components disrupts this intricate network, increasing costs and causing delays. This disruption challenges the traditionally efficient just-in-time manufacturing and delivery schedules critical to the industry.
Rising Costs and Production Delays
Import duties on aircraft materials and parts have driven up manufacturing costs for Boeing and its suppliers. As costs rise, aircraft production timelines are becoming less predictable, affecting delivery commitments to airlines worldwide.
The associated uncertainty can ripple throughout the supply chain, impacting inventory management, suppliers’ cash flow, and contractual obligations.
Shifting Market Dynamics
With Boeing’s exposure to China decreasing, currently representing about 10% of its backlog due to tariff-driven order cancellations, its European competitor, Airbus, is capitalizing on the opportunity.
Airbus is actively negotiating with Chinese airlines for substantial orders, possibly securing contracts for up to 500 jets, illustrating how the tariffs are reshaping competitive dynamics in the global aerospace market.
Simplify global supply chain challenges with our technology-driven freight solutions.
Get a Quote!Boeing and Stakeholder Responses to US-China Civilian Aircraft Tariffs
The delivery freeze has forced Boeing and industry stakeholders to respond with urgent, high-stakes strategies.
Boeing’s Strategic Actions Amid Delivery Freeze
In response to halted deliveries caused by retaliatory tariffs, Boeing’s CEO, Kelly Ortberg, confirmed that the company is actively exploring options to re-market or reassign approximately 41 built or in-production aircraft that Chinese customers are no longer accepting.
Boeing has taken a firm stance, stating it will not continue manufacturing jets for customers unwilling to take delivery, highlighting the serious operational disruption from ongoing trade tensions.
Seeking Alternative Markets Beyond China
Boeing is intensifying efforts to pivot towards alternative markets such as India, Southeast Asia, and Latin America. However, experts caution that re-selling these jets is complex due to extensive buyer-specific customizations, cabins, avionics, and other configurations, meaning the resale process will involve substantial costs and logistical negotiations.
Among potential new buyers, Air India Express has been identified, signaling emerging demand outside China’s market.
Ongoing Engagement with the US Government and Diplomacy
Boeing maintains daily communication with US government officials, including cabinet secretaries and the President’s office, to coordinate responses to the trade disruptions.
Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent has expressed optimism about the prospect of a “big deal” to ease trade tensions with China, indicating potential diplomatic resolution on tariffs impacting the aerospace sector.
Advice for Exporters and Logistics Professionals
This evolving scenario reinforces the need for exporters and supply chain managers to:
- Be adaptable in managing shipment rerouting and supply disruptions.
- Monitor regulatory and geopolitical developments closely.
- Manage contractual and logistical risks proactively in an uncertain tariff environment.
- Adopt flexible, technology-enabled logistics solutions to quickly respond to rerouting or compliance.
Partnering with reliable freight forwarders like Intoglo can help manage rerouting, customs complexities, and compliance in a volatile tariff environment.
Optimize your cross-border shipping strategy with Intoglo’s expert support.
Contact us today!What Exporters and Aviation Stakeholders Need to Know About US-China Tariff Impacts
For exporters, manufacturers, and aviation stakeholders, the Boeing-China fallout highlights broader lessons about navigating trade uncertainty.
Key Risks for Exporters and Manufacturers
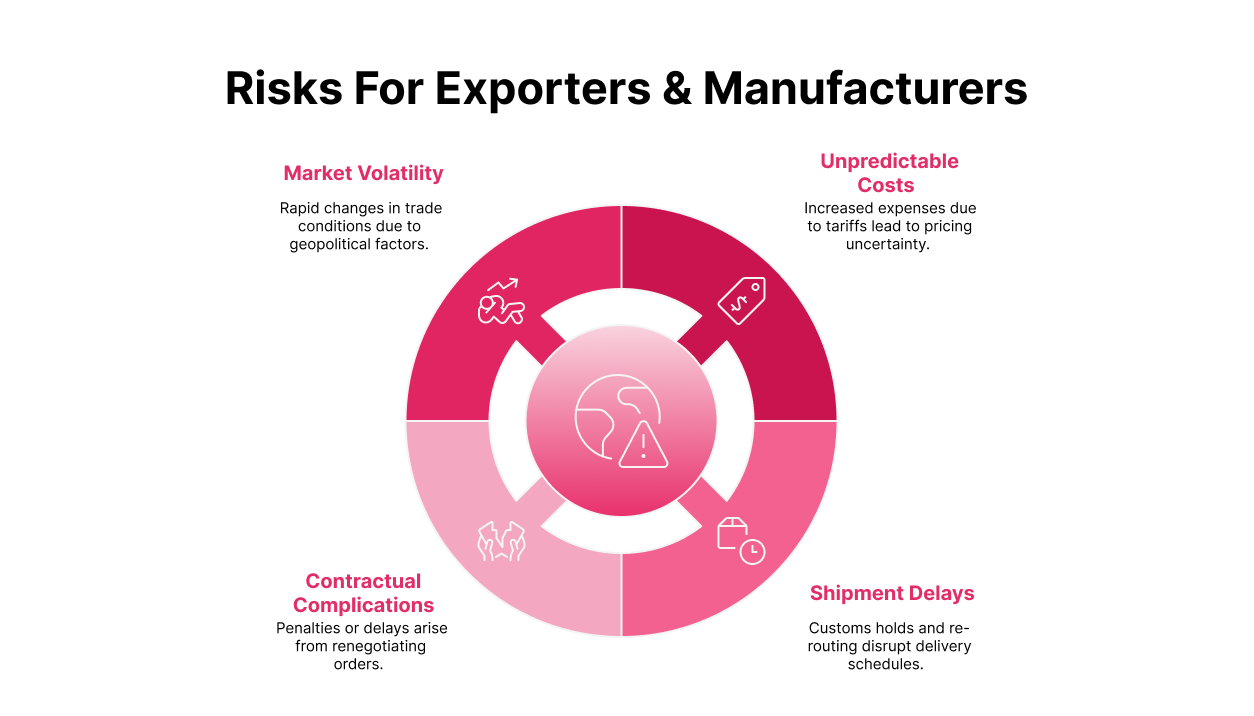
The escalating tariffs and delivery disruptions expose exporters and manufacturers to several risks:
- Unpredictable costs: Increased landed costs due to tariffs raise pricing uncertainty.
- Shipment delays: Customs holds and re-routing of aircraft affect delivery schedules.
- Contractual complications: Re-negotiating or reallocating orders may incur penalties or delays.
- Market volatility: Changing geopolitical factors can rapidly alter trade conditions.
Strategic Recommendations
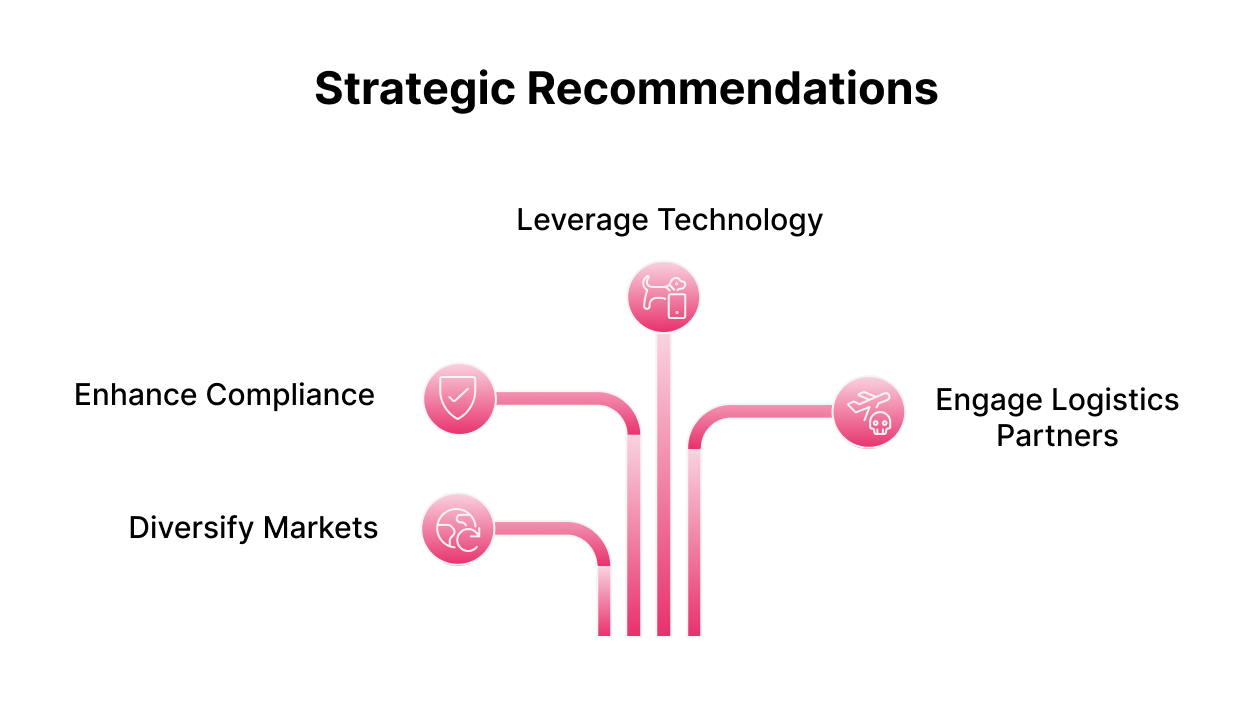
To navigate these challenges, exporters and aviation industry players should:
- Diversify markets and supply chains: Seek alternative buyers and suppliers beyond China and the US.
- Enhance regulatory compliance: Stay updated on tariff changes and customs compliance requirements.
- Leverage technology for visibility: Adopt real-time shipment tracking and tariff classification tools to reduce risks.
- Engage proactive logistics partners: Collaborate with freight forwarders familiar with trade complexities to ensure smoother operations.
Also Read: China Exports to the US: Trends and Trade Impact
How Intoglo Supports Your Export Goals Amid Tariff Challenges
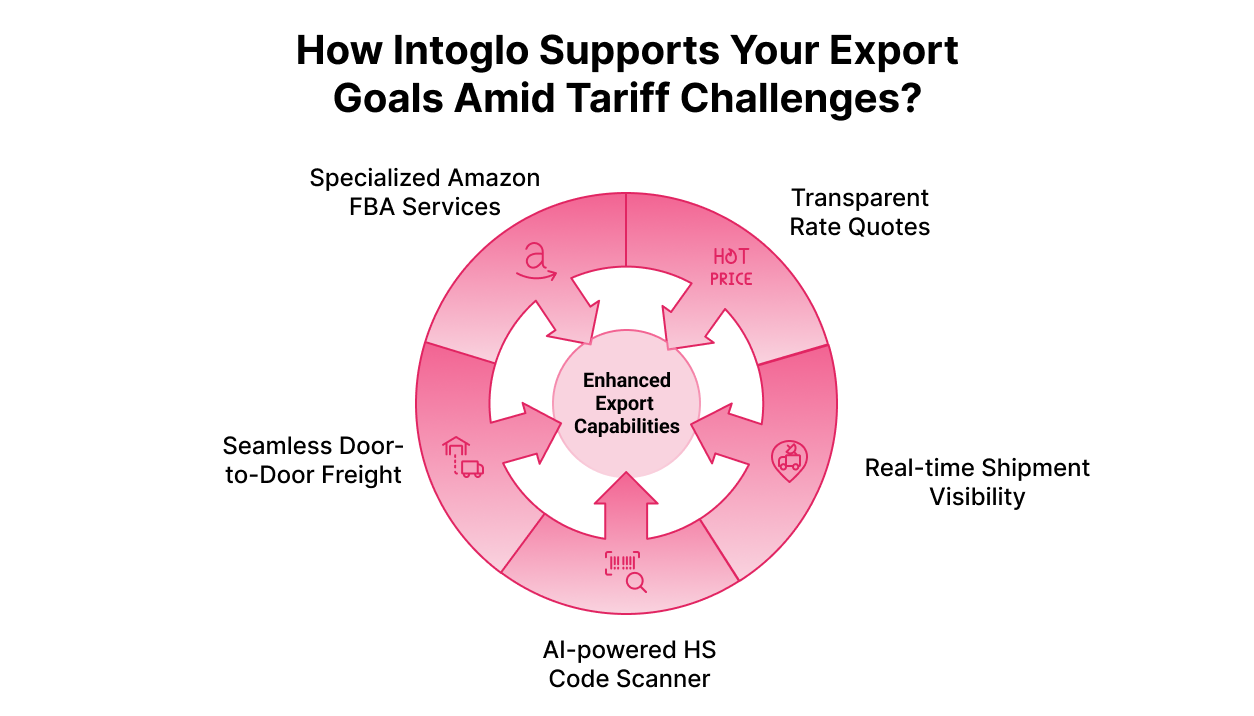
Intoglo, a technology-driven digital freight forwarder, offers comprehensive end-to-end logistics solutions tailored to exporters navigating complex international trade environments. With Intoglo, you gain:
- Instant, transparent rate quotes directly from shipping lines, eliminating hidden fees.
- Real-time shipment visibility and proactive notifications through the proprietary Glotrack platform.
- AI-powered HS Code scanner for accurate product classification and duty estimation.
- Seamless door-to-door FCL ocean freight from India to the US, with expert customs clearance support.
- Specialized Amazon FBA shipping services for D2C brands and sellers targeting the US market.
Partnering with Intoglo ensures agility, cost control, and compliance — critical advantages in a volatile trade landscape shaped by US-China tariffs.
Conclusion
The 2025 US-China trade war has fundamentally altered the global landscape for civilian aircraft manufacturing and exports. Boeing faces unprecedented delivery disruptions as Chinese airlines halt jet acceptance amid retaliatory tariffs, while the broader aerospace supply chain grapples with rising costs and operational uncertainties.
For exporters, manufacturers, and logistics professionals, the evolving tariff environment demands adaptability, risk awareness, and strategic diversification.
Preparing for shifts in markets, compliance protocols, and operational demands is essential to maintaining resilience and competitiveness in this volatile era of global trade.
Stay Ahead in Aerospace Trade and Logistics
Connect with our team to optimize your supply chain strategy and safeguard your aviation exports today.
FAQs
1. What triggered the imposition of tariffs on civilian aircraft in the US-China trade war?
The tariffs stem from escalating trade tensions in 2025, when the US targeted high-value Chinese imports, including civilian aircraft, to address trade imbalances and leverage negotiations. China responded with tariffs on US products like Boeing jets as part of broader economic and geopolitical disputes.
2. How have Boeing’s operations been affected by China’s refusal to accept aircraft deliveries?
Chinese airlines have stopped taking delivery of Boeing jets, forcing Boeing to return completed aircraft and pause production for some orders. This disrupted Boeing’s supply chain, increased backlog complexity, and led to efforts to resell jets in other markets.
3. What challenges does Boeing face in redirecting aircraft initially intended for the Chinese market?
Redirecting jets involves overcoming costly reconfigurations to meet new customers’ specifications, navigating legal and contractual bindings, and managing logistical complexities. These hurdles slow Boeing’s ability to quickly recover revenue from undelivered planes.
4. How do these tariffs impact global aerospace suppliers outside the US and China?
The aerospace supply chain spans multiple countries, including France, Canada, the UK, Japan, and Italy, many of which now face indirect tariff impacts. Increased duties disrupt component sourcing, raise production costs, and complicate inventory management for manufacturers.
5. What practical steps can exporters take to reduce risks amid ongoing tariff uncertainties?
Exporters should diversify markets and supply sources, stay informed on tariff changes, employ technology for accurate customs classification and shipment visibility, and collaborate with logistics partners experienced in managing complex trade lanes.









Leave a comment